Electric bikes are getting more popular, but many wonder if they can ride on city streets. The answer is not simple, as laws about e-bikes differ across the U.S. It can be hard to understand all the rules at the federal, state, and local levels. But don’t worry, this guide will help you understand e-bike laws. This way, you can ride safely and follow the law.
In This Article:
Understanding Federal E-Bike Regulations
The federal government sets the rules for electric bikes (e-bikes) on U.S. roads. The Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) makes these rules. An e-bike is considered a “low-speed electric bicycle” if it meets certain criteria.
It must have fully operable pedals, an electric motor under 750 watts, and a top speed of 20 mph. This speed is when the motor is the only power source.
The CPSC also has safety standards for e-bikes. These include mechanical strength, electrical systems, and labeling. But, states can make their own rules, leading to different laws in each state.
This means e-bike riders face different rules when traveling between states. It’s like a patchwork of rules to follow.
Federal Power and Speed Limitations
The federal rules allow e-bikes with motors up to 750 watts. They also set a top speed of 20 mph when the motor is the only power source. This is different from the European Union’s rules, which are stricter.
Consumer Protection Guidelines
The CPSC also has guidelines to protect consumers. These guidelines require e-bike makers to label their products clearly. They must include information like motor wattage, top speed, and other important details.
As the e-bike market grows, it’s crucial for riders to know the latest rules. These rules cover legal electric bike specifications and e-bike road legality. Knowing these electric bicycle laws ensures a safe and legal ride.
The Three-Class E-Bike Classification System Explained
Understanding electric bikes (e-bikes) can be a bit confusing. But knowing the three-class system is key to making sure your e-bike is legal. This system, used by over 30 states, outlines what each e-bike can do and where it can go.
The three classes are as follows:
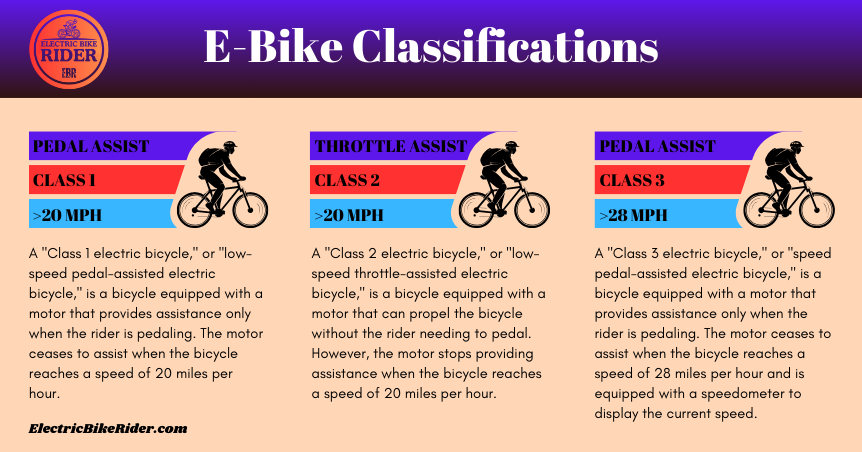
- Class 1 e-bikes have a motor that helps when you pedal, but only up to 20 mph. They offer a great ride and are often allowed on bike paths and trails.
- Class 2 e-bikes have both pedal-assist and a throttle, also up to 20 mph. They follow the same rules as regular bikes, so you can ride them on bike lanes and shared paths.
- Class 3 e-bikes also have pedal-assist and a throttle, but they can go up to 28 mph. They are the fastest legal e-bikes, but they have rules like age limits and where you can ride them.
| E-Bike Class | Motor Assist | Top Speed | Key Regulations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | Pedal-assist only | 20 mph | Allowed on most bike paths and trails |
| Class 2 | Pedal-assist and throttle | 20 mph | Compliant with traditional bicycle road rules |
| Class 3 | Pedal-assist and throttle | 28 mph | Subject to age limits and trail access restrictions |
It’s important to know about these classes. The rules and where you can ride can change a lot. By learning about the three-class system, you can make sure your e-bike is street-legal and enjoy riding it.
Are Electric Bikes Street Legal: State-by-State Overview
In the United States, electric bikes have different rules in each state. Some states follow a three-tier system for e-bikes, while others have not. It’s important for riders to know the local laws to ride safely and legally.
Popular State Regulations
More than half of the US states use a 3-tier system for e-bikes. Class 1 e-bikes, which help you pedal up to 20 mph, usually don’t need a license. Class 2 e-bikes, with a throttle up to 20 mph, also often don’t need a license. But Class 3 e-bikes, which can go up to 28 mph, might need a license in many places.
Legal Age Requirements
The age to ride an electric bike varies by state. For example, Idaho lets 15-year-olds ride, while New Jersey also sets the age at 15 for Class 3 e-bikes. Florida, however, lets 16-year-olds ride without a license.
Registration and Licensing Rules
Rules for registering and licensing e-bikes also differ by state. Some states, like Alaska, Hawaii, and New Jersey, have special rules for Class 3 e-bikes. Florida, on the other hand, doesn’t require a license or registration, and helmets are only needed for riders over 16.
| State | License Requirement | Age Requirement | Registration |
|---|---|---|---|
| California | No license currently, but changes may be coming soon | No age limit | No registration required |
| Alaska | Class M license required for e-bike operation | No age limit | Registration required |
| Florida | No license required | 16+ for operation | No registration required |
| New Jersey | Operator’s license required for Class 3 e-bikes | 15+ for Class 3 e-bikes | No registration required |
E-Bike Power and Speed Restrictions
Electric bikes have rules about power and speed. These rules help decide if they’re legal and where you can ride them. It’s key for e-bike owners to know these laws to ride safely and legally.
The U.S. government sets limits for low-speed electric bikes. They can’t go faster than 20 mph and have an electric motor under 750 watts. This rule matches the electric bike traffic rules and legal e-bike specifications from the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC).
But, these rules change from state to state. Over 30 states have their own rules for electric bikes. For example, Class 3 e-bikes can go up to 28 mph in many places. On the other hand, Class 1 and 2 e-bikes are capped at 20 mph.
| E-Bike Class | Motor Power | Top Speed | Throttle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | 750W | 20 mph | No |
| Class 2 | 750W | 20 mph | Yes |
| Class 3 | 750W | 28 mph | No |
E-bike riders need to know the ebike regulations in their area. This ensures they ride legally and safely. Breaking these rules can lead to fines, penalties, or even legal trouble.
Where You Can Legally Ride Your E-Bike
As electric bikes (e-bikes) become more popular, knowing where to ride them is key. The rules for riding e-bikes on roads, trails, and sidewalks differ. This depends on local laws and your e-bike’s class.
Road Access Guidelines
Most U.S. states let you ride electric bikes on public roads. E-bikes are treated like regular bikes, with riders needing to follow traffic laws. But, the rules on electric bike street accessibility can change based on your e-bike’s class. Some models might only be allowed in bike lanes or cycling paths.
Trail and Path Regulations
Getting to trails and bike paths can be tricky. Many states use a three-class system for e-bikes, with different rules for each. For instance, in California, Class 1 and Class 2 e-bikes are okay on bike paths. But, Class 3 e-bikes are only for roads and bike lanes. Always check city ordinances on e-bikes before riding on trails or bike paths.
Sidewalk Usage Rules
The rules for e-bikes on sidewalks vary a lot in the U.S. In places like New York City, all e-bike classes are banned on sidewalks for safety. Other areas might let e-bikes on sidewalks but with speed limits or class restrictions. It’s important to know the city ordinances on e-bikes before using sidewalks.
It’s crucial to stay updated on local bike laws. Look for reliable info on state and city transportation websites, local bike shops, or cycling clubs. This will help you understand the riding electric bikes on public roads, electric bike street accessibility, and city ordinances on e-bikes in your area.
Safety Equipment and Legal Requirements
Riding an e-bike requires a focus on safety. Laws about electric bicycle compliance differ by state. Yet, there are key e-bike safety guidelines for a safe ride.
Wearing a helmet is a must for e-bike riders. States like Maryland, Louisiana, Massachusetts, West Virginia, and Connecticut have helmet laws. These laws apply to young riders and those on Class 3 electric bicycles. Always check local laws to follow legal restrictions on e-bike usage.
Other safety gear like lights, reflectors, and brakes might be needed in some places. Keeping these items in good working order is vital. It ensures the safety of e-bike riders and others on the road.
It’s important to follow traffic laws and stay alert while riding. Adhering to speed limits, signaling, and yielding to others can prevent accidents. This makes for a safe and fun electric bicycle experience.
| State | Helmet Requirement | Min. Rider Age | Speed Limit |
|---|---|---|---|
| California | No helmet required | No age restriction | Class 1 & 2: 20 mph, Class 3: 28 mph |
| New York | Helmets required for riders under 18 | No age restriction | Class 1 & 2: 20 mph, Class 3: 25 mph in cities over 1 million |
| Florida | No helmet required | 16 years old | Class 1 & 2: 20 mph, Class 3: 28 mph |
Knowing the e-bike safety guidelines and legal restrictions on e-bike usage in your area is key. This way, electric bicycle riders can enjoy the ride safely and legally.
Insurance and Registration Requirements for E-Bikes
When it comes to electric bike registration and e-bike licensing, the rules can change a lot from state to state. Many places don’t need you to register or insure your e-bike if it follows federal rules. But, some places have extra legal requirements for ebikes you need to follow.
State-Specific Insurance Rules
In most US states, you don’t need insurance for e-bikes that follow federal rules. But, if your e-bike goes too fast or has too much power, it might be seen as a moped or motorcycle. Then, you’ll need insurance like you would for a car. California, for example, has its own rules for e-bike insurance based on how you use it. Always check your state’s laws to make sure you’re following them.
Registration Processes
Like insurance, whether you need to register your electric bike depends on its type and your state’s laws. Usually, e-bikes that follow federal rules don’t need to be registered. But, some states might have special rules for e-bikes, especially if they’re too fast or powerful. Make sure to look up your local laws to know what’s needed for your e-bike.
Documentation Needed
The papers you need for e-bike licensing and registration can differ. You might need to show proof of ownership, like a receipt, and a form of ID, like a driver’s license. Some places might ask for more details, like your e-bike’s make and model number. Always check with your state or local government to find out what you need for your e-bike.
“E-bikes are a game-changer for personal transportation, but it’s crucial to understand the legal requirements for ebikes in your state or city to ensure safe and compliant riding.”
Legal Consequences of Non-Compliance
Every electric bike owner must understand the rules of legal ebike operation, e-bike laws and regulations, and ebike road rules. Not following these can lead to serious legal issues.
Riding an e-bike that’s too fast or powerful without the right papers can get you in trouble. You might face fines or even jail time. This depends on the laws in your area and how bad the offense is.
Also, riding in places where e-bikes are not allowed can cost you a lot. It’s important to know where you can ride to avoid fines or other legal problems.
| Violation | Potential Consequences |
|---|---|
| Exceeding legal power or speed limits | Fines, impoundment, or criminal charges (e.g., driving without a license) |
| Riding in prohibited areas | Fines, warnings, or restrictions on e-bike usage |
| Failure to wear required safety equipment | Fines, citations, or inability to operate the e-bike legally |
To avoid legal issues, e-bike riders should know the e-bike laws and regulations in their area. Knowing the legal ebike operation rules and ebike road rules makes riding safer and more enjoyable.
By staying informed and following the rules, electric bike fans can enjoy their rides without legal worries. Following the legal ebike operation rules is not just the right thing to do. It also helps avoid unnecessary problems later on.
International E-Bike Laws Comparison
Electric bikes (e-bikes) are becoming more popular around the world. But, the laws about using them vary a lot from country to country. It’s important for riders to know the regulations on electric bikes, e-bike road rules, and the legal status of electric bikes to stay safe and legal.
In the United States, e-bikes are divided into three types. Class 1 e-bikes help when you pedal and stop at 20 mph. They are allowed on bike paths and trails. Class 2 e-bikes help without pedaling but also stop at 20 mph. Class 3 e-bikes go up to 28 mph and have stricter rules, like needing helmets and age limits.
In the European Union, e-bikes with a 250W motor and up to 25 km/h speed are seen as bikes. But, each country in the EU can have its own rules. For example, Belgium has three types of e-bikes with different rules for speed, motor power, and safety gear.
In Asia, like in Japan, you need a license and must wear a helmet. In China, the biggest e-bike market, you must register your e-bike. There’s a 25 km/h speed limit, and e-bikes can’t be on highways or in nature reserves.
In Australia, e-bikes are seen as a mix between bikes and mopeds. They don’t need a license or registration but have speed limits and age rules for safety.
Worldwide, e-bike laws are different and complex. The US has a three-class system, the EU has more consistent rules, Asia has varied laws, and Australia has a balanced approach. E-bike owners should check the regulations on electric bikes, e-bike road rules, and the legal status of electric bikes in their area, whether at home or abroad.
| Region | Motor Output Limit | Maximum Assisted Speed | Licensing/Registration | Helmet Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Class 1: Pedal-assist only, 750W Class 2: Throttle-assist, 750W Class 3: Pedal-assist, 750W |
Class 1: 20 mph Class 2: 20 mph Class 3: 28 mph |
Varies by state | Class 3: Required |
| European Union | 250W | 25 km/h (15.5 mph) | Varies by country | Varies by country |
| Australia | 200-250W | 25 km/h (15.5 mph) | No license or registration required | Age-dependent |
| Canada | 500W | 32 km/h (20 mph) | Varies by province | Varies by province |
The world of e-bike regulations, e-bike road rules, and the legal status of electric bikes is complex and varied. Each place has its own rules and requirements. As e-bikes become more popular, it’s key for riders to know and follow the local regulations on electric bikes to ride safely and legally.
Future of E-Bike Legislation
Electric bicycles are becoming more popular, leading to changes in laws. Lawmakers are working to keep up with these changes. They aim to make new rules that will guide the future of e-bike laws in the U.S.
Emerging Trends
One big trend is the push for standard e-bike classifications. Many states are following the CPSC’s three-class system. This system is based on power and speed, making rules more uniform for laws governing electric bicycles.
Another trend is clearer rules for electric bike street use. Policymakers want to ensure e-bikes are used safely on roads and paths. This is important as more people start using e-bikes.
Proposed Changes
Some states are looking to update their e-bike laws. They might change speed limits, age rules, and trail access. These changes aim to balance the benefits of e-bikes with safety concerns.
New York State has made new laws for e-bikes. They include penalties for retailers and safety rules for lithium-ion batteries. This is to prevent fires and accidents.
Industry Impact
The e-bike industry is helping shape new laws. They work with policymakers to create fair rules. This ensures e-bikes are safe and popular.
As laws change, it’s key for e-bike users to stay updated. They should follow the latest rules in their area.
“Unaddressed battery dangers have led to numerous fires in local communities, emphasizing the importance of new legislation to enhance safety protocols for using lithium-ion batteries and streets.”
– State Senator Iwen Chu
| Year | Lithium-Ion Battery-Related Fires in New York City | Injuries | Fatalities |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 222 | 88 | 4 |
| 2023 | 224 | 122 | 14 |
Conclusion
Electric bike laws are changing, and riders need to keep up. Laws about e-bikes differ a lot from place to place. This makes it important to know the rules in your area.
It’s key to understand the different types of e-bikes and their limits. Knowing the speed and power rules helps you ride safely and legally. For example, California, Florida, and Illinois have their own rules for e-bikes.
As e-bikes get more advanced, laws will likely change too. Keeping an eye on updates about are electric bikes street legal, electric bike laws, and e-bike regulations is important. This way, you can ride safely and follow the law.